
- FREEMAT DRAW GRAPHICS HOW TO
- FREEMAT DRAW GRAPHICS FULL
- FREEMAT DRAW GRAPHICS SOFTWARE
- FREEMAT DRAW GRAPHICS CODE
Core graphics objects include basic drawing primitives such as line, text, rectangles, patches (filled polygons), surfaces (3D grid of vertices), images (2D matrix representation of an image), light sources, and axes (define the coordinate system). There are two basic types of graphics objects in the MATLAB graphics model: Core graphics objects and Composite graphics objects. In MATLAB graphics objects are used to create visual representations of data. This insures cross-platform portability and creates a device independent graphics layer.
FREEMAT DRAW GRAPHICS SOFTWARE
MATLAB has an abstract graphics layer above the local host's graphic software interface.
FREEMAT DRAW GRAPHICS HOW TO
This will tell you on what machines MATLAB is available, how to set up your environment, how to set your display, and where the documentation is. By playing with the example code, you will gain a deeper understanding of how the various graphic functions work.īoston University SCV users, please go to the SCV MATLAB Help Page for information specific to the installation at this site.
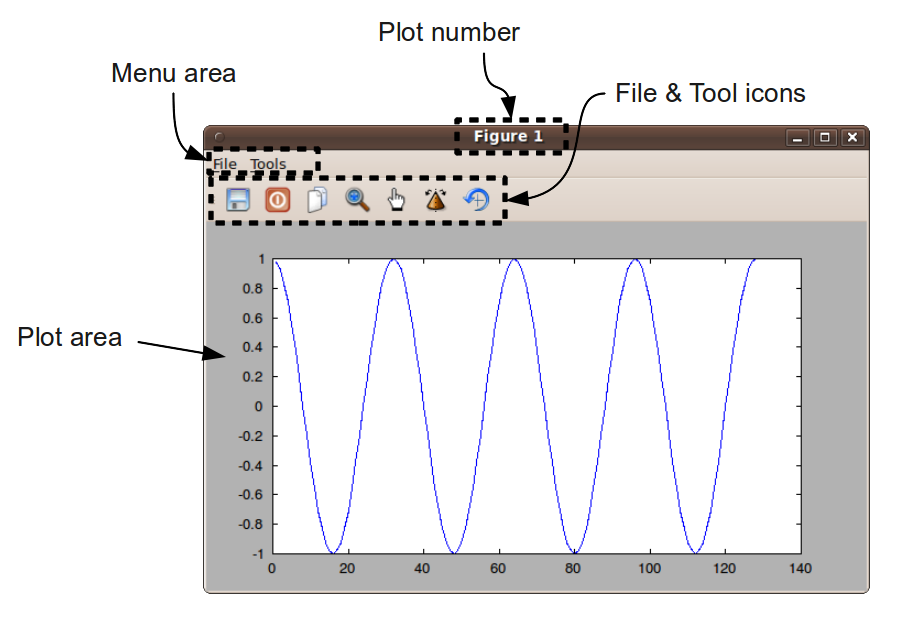
FREEMAT DRAW GRAPHICS CODE
After browsing the documentation, you should then experiment with the example code by varying some of the arguments and watching the effect this has on the output. It will also be helpful for you to browse the MATLAB documentation for the specific functions as we discuss them (links are provided). This can be accomplished by copying and pasting the listed example code into the MATLAB Command Window. The most effective way for you to go through this tutorial is to run the listed example code in a MATLAB session as you proceed through the tutorial.

FREEMAT DRAW GRAPHICS FULL
And there is a full set of documentation available from within MATLAB itself which can be viewed by selecting Product Help from the Help menu. MathWorks, the developer of MATLAB, also has extensive MATLAB documentation including video tutorials on its website. It is assumed that the student is familiar with the basics of using MATLAB.įor an introductory tutorial on using MATLAB, see the SCV tutorial an Introduction to MATLAB. We will cover major visualization techniques such as slicing, color mapping, contouring, oriented glyphs, and streamlines. In this tutorial we will use the command interface to show how to visualize scientific data using MATLAB graphics commands. You can either use the MATLAB GUI plotting tools to interactively create graphs (see Some Ways to Use Plotting Tools for more information) or you can use the command interface by entering MATLAB graphics commands in the Command Window. There are two basic ways to create graphs in MATLAB. It includes high-level functions for two-dimensional and three-dimensional data visualization, image processing, animation, and presentation graphics. MATLAB has extensive facilities for displaying vectors and matrices as graphs, as well as annotating and printing these graphs. MATLAB is an interactive system whose basic data type is the array or matrix. It integrates computation, visualization, and programming in an easy-to-use environment where problems and solutions are expressed in common mathematical notation. MATLAB is a high-performance language for technical computing. Slicing Scalar Visualization Algorithms Color MappingĬontours/Isosurfaces Vector Visualization Algorithms Oriented Glyphs Lighting MATLAB Data Types Modeling Visualization Algorithms Matrix to Surface Graphics Model Creating a Graphics Window

Getting started A few basic hints that will help you get started. % % This function generates a candlestick chart for a given O,H,L,C data % D is dates % O is open % H is high % L is low % C is close % symbol % % Example: % =get_symbol_data('F',150) % gen_chart(D,O,H,L,C,'F') % % % Copyright 2010 EdgeMe % $Revision: 1.0.0.Table of Contents Introduction A brief introduction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
